Fibroid
Fibroids are benign uterine tumors that may lead to heavy menstrual bleeding.
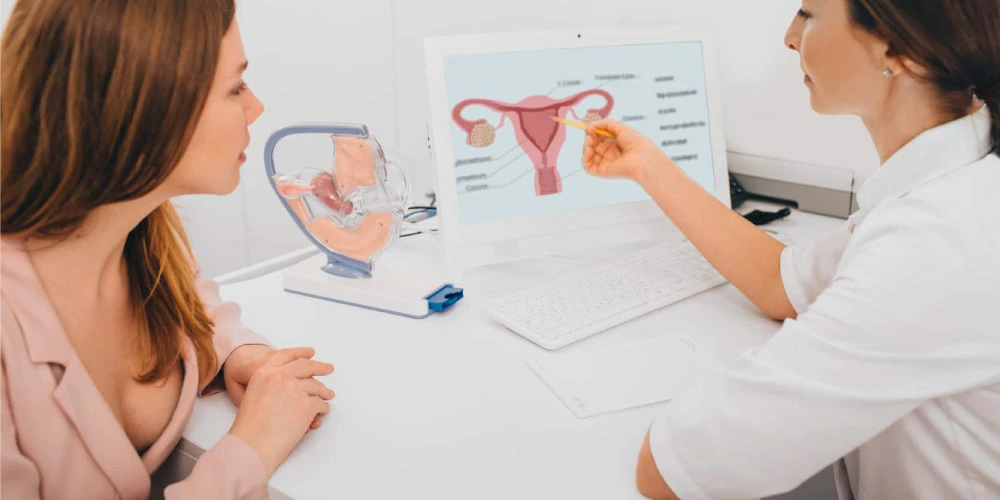
What are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas or myomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus. These benign tumors are made up of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue and can vary in size from tiny seedlings to large masses that can distort and enlarge the uterus. While fibroids are common and often asymptomatic, they can sometimes cause significant discomfort and health issues.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
Many women with fibroids experience no symptoms, but when symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia): Excessive bleeding during menstruation, sometimes with blood clots.
- Prolonged menstrual periods: Menstrual bleeding lasting more than a week.
- Pelvic pain and pressure: Discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the pelvic region.
- Frequent urination: Pressure on the bladder can cause a frequent need to urinate.
- Constipation: Pressure on the rectum can lead to difficulty with bowel movements.
- Backache or leg pains: Pain in the lower back or legs due to pressure on nearby nerves.
- Enlarged abdomen: A noticeable increase in abdominal size.
Types of Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids are classified based on their location within the uterus:
- Intramural fibroids: Develop within the muscular wall of the uterus and are the most common type.
- Subserosal fibroids: Grow on the outer surface of the uterus and can sometimes become quite large.
- Submucosal fibroids: Develop just beneath the lining of the uterine cavity and can interfere with menstrual bleeding and fertility.
- Pedunculated fibroids: Attached to the uterine wall by a stalk-like structure and can grow either inside or outside the uterus.
Causes of Uterine Fibroids

The exact cause of uterine fibroids is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to their development:
- Hormonal factors: Estrogen and progesterone, hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, promote the growth of fibroids.
- Genetic factors: A family history of fibroids increases the likelihood of developing them.
- Other growth factors: Substances in the body that help maintain tissues may also affect fibroid growth.
- Extracellular matrix (ECM): The material that makes cells stick together can promote fibroid growth.
Diagnosis of Uterine Fibroids
Diagnosing fibroids typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests:
- Pelvic examination: A doctor can often feel irregularities in the shape of the uterus.
- Ultrasound: Imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of the uterus and detect fibroids.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Detailed images of the uterus to determine the size and location of fibroids.
- Hysterosonography: Uses saline to expand the uterine cavity, making it easier to get images of submucosal fibroids.
- Hysterosalpingography: Involves injecting a dye into the uterus and fallopian tubes to highlight the uterine cavity on X-ray images.
- Hysteroscopy: A thin, lighted scope inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus to examine the inside of the uterus.
Treatment of Uterine Fibroids
The treatment of uterine fibroids depends on the size, location, symptoms, and the woman's desire to maintain fertility. Options include:
Medications
- Hormonal therapies: Birth control pills, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, and other hormonal treatments can help regulate the menstrual cycle and shrink fibroids.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Help relieve pain and reduce bleeding.
- Tranexamic acid: Reduces heavy menstrual bleeding.
Non-Surgical Procedures
- Uterine artery embolization (UAE): Blocks the blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
- MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery (FUS): Uses high-intensity ultrasound waves to destroy fibroid tissue.
Surgical Procedures
- Myomectomy: Surgical removal of fibroids while preserving the uterus, suitable for women who wish to maintain fertility.
- Hysterectomy: Complete removal of the uterus, which is a definitive treatment for fibroids but eliminates the possibility of pregnancy.
- Endometrial ablation: Destroys the lining of the uterus to reduce heavy bleeding but is not suitable for women who wish to maintain fertility.